Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 15: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Practice Book for KVPY Aptitude Test - Stream SA Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Geometrical Optics, Exercise 2: Exercise 2 with Hints & Solutions
A cubical vessel has opaque walls. An observer (dark circle in the figure below) is located such that she can see only the wall but not the bottom. Nearly to what height should water be poured so that she can see an object placed at the bottom at a distance of from the corner ? (Refractive index of water is .
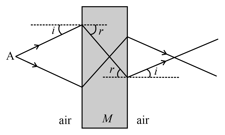
Electromagnetic waves emanating from a point (in air) are incident on a rectangular block of material and emerge from the other side as shown. The angles and are angles of incidence and refraction when the wave travels from air to the medium. Such paths for the rays are possible
A hollow lens is made of thin glass and in the shape of a double concave lens. It can be filled with air, the water of refractive index or of refractive index . It will act as a diverging lens if it is
Mercury is often used in clinical thermometers. Which one of the following properties of mercury is not a reason for this?
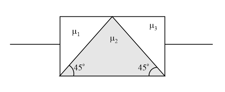
A rectangular block is composed of three different glass prisms (with refractive indices and ) as shown in the figure below. A ray of light incident normal to the left face emerges normal to the right face. Then the refractive indices are related by-
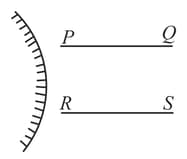
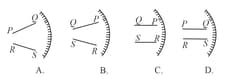
A person looks at the image of two parallel finite length lines and in a convex mirror (see figure)
Which of the following represents schematically the image correctly? (Note : letters and are used only to denote the endpoints of the lines.)
Let and are written on cardboard as shown in the picture.
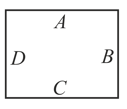
The cardboard is kept at a suitable distance behind a transparent empty glass of cylindrical shape. If the glass is now filled with water, one sees an inverted image of the pattern on the cardboard when looking through the glass. Ignoring the magnification effect, the image would appear as
A glass beaker is filled with water up to . It is kept on top of a thick glass slab. When a coin at the bottom of the glass slab is viewed at the normal incidence from above the beaker, its apparent depth from the water surface is . Value of is close to (the refractive indices of water and glass are and respectively)
